Remote work has transitioned from a niche concept to a mainstream mode of employment, particularly in the last few years. As technology advanced and the world became more connected, the idea of working from anywhere began to take hold. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, pushing organizations worldwide to adopt remote work practices almost overnight. But now, with the pandemic largely behind us, the question remains: Is remote work here to stay?
The Rise of Remote Work
Historical Context
Remote work isn’t a new concept. It traces its roots back to the late 20th century when telecommuting first became possible thanks to advancements in technology. In the 1970s and 1980s, the introduction of personal computers and the internet began to break down the barriers of traditional office spaces. However, it was still a niche practice, primarily limited to specific industries like IT and consulting.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic was a game-changer for remote work. Almost overnight, millions of workers worldwide were forced to work from home as offices shut down to prevent the spread of the virus. Companies that had never considered remote work before were suddenly implementing it on a large scale. This rapid transition highlighted both the feasibility and potential benefits of remote work, leading to a significant shift in workplace norms.
Current Trends in Remote Work
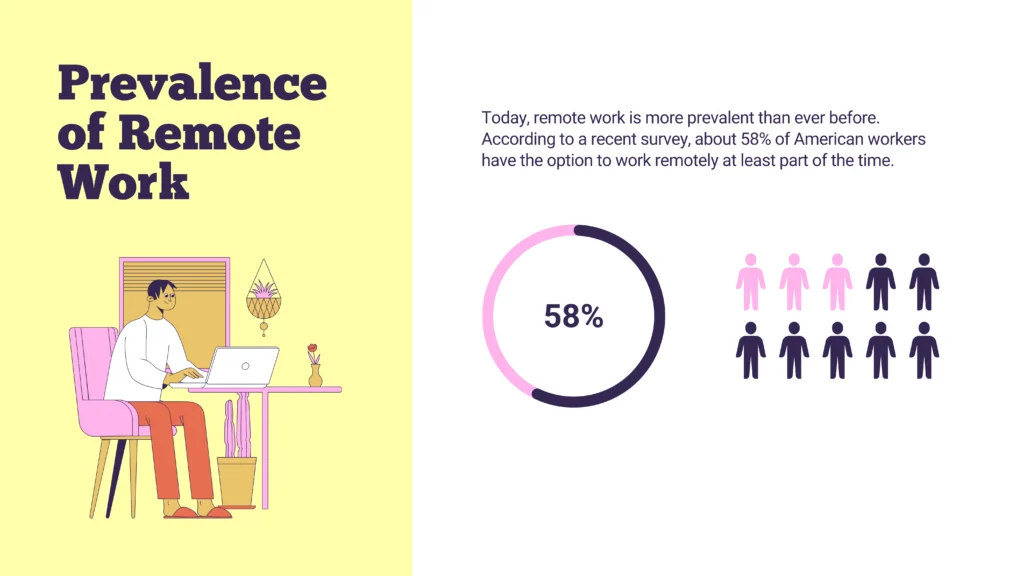
Prevalence of Remote Work
Today, remote work is more prevalent than ever before. According to a recent survey, about 58% of American workers have the option to work remotely at least part of the time. This trend isn’t limited to the United States; countries around the world are seeing a similar shift. Industries like technology, finance, and creative services are leading the charge, with many companies opting for fully remote or hybrid work models.
Worker Preferences
Employees have quickly adapted to remote work and, in many cases, prefer it to traditional office settings. The flexibility that remote work offers has become a significant factor in job satisfaction. Workers appreciate the ability to manage their schedules, avoid long commutes, and better balance their work and personal lives. A survey found that 70% of employees would like to continue working remotely, even after the pandemic.
Industry Adaptation
Different industries have adapted to remote work in various ways. While tech companies were quick to embrace remote work, traditional industries like manufacturing and healthcare have found it more challenging. However, even these sectors are finding ways to incorporate remote work, particularly for roles that don’t require physical presence. Technology plays a crucial role in this adaptation, with tools like video conferencing, project management software, and cloud services enabling seamless remote collaboration.
Company Policies
In response to the growing demand for remote work, many companies have updated their policies to accommodate this new norm. Tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Facebook have adopted hybrid models, allowing employees to split their time between the office and home. Other companies have gone fully remote, abandoning their physical offices altogether. These new policies reflect a broader recognition that remote work is not just a temporary trend but a permanent shift in how we work.
Future Projections for Remote Work
Long-term Sustainability
Is remote work here to stay? The answer seems to be a resounding yes. Experts predict that remote work will continue to be a significant part of the workplace landscape. Several factors will influence its sustainability, including advances in technology, changes in workplace culture, and ongoing demand from employees. However, the extent to which remote work remains prevalent will vary by industry and region.
Evolving Workplace Dynamics
As remote work becomes more common, workplace dynamics are likely to evolve. The traditional office setup, with its cubicles and meeting rooms, may give way to more flexible and dynamic environments. Communication and collaboration will also change, with a greater reliance on digital tools and platforms. However, these changes come with challenges, such as maintaining company culture and ensuring effective communication across dispersed teams.
Benefits of Remote Work
Increased Productivity
One of the most significant benefits of remote work is the potential for increased productivity. Numerous studies have shown that remote workers often outperform their in-office counterparts. Without the distractions of a traditional office environment, employees can focus more on their tasks and complete them more efficiently. Additionally, remote work allows for a better work-life balance, which can lead to higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates.
Cost Savings
Remote work offers cost savings for both employers and employees. Companies can reduce overhead costs by downsizing their office space or eliminating it. This can result in significant savings on rent, utilities, and office supplies. Employees, on the other hand, can save money on commuting, meals, and work attire. These cost savings make remote work an attractive option for both parties.

Access to a Global Talent Pool
Remote work opens up opportunities to hire talent from anywhere in the world. Companies are no longer limited by geography when searching for the best candidates. This access to a global talent pool can lead to more diverse and innovative teams. Moreover, remote work allows companies to tap into markets they might not have considered before, further expanding their reach and potential.
Challenges of Remote Work
Communication and Collaboration Issues
Despite the many benefits, remote work does come with its challenges. Communication and collaboration can be more difficult when team members are not in the same physical space. Miscommunications can arise, and it can be harder to build and maintain relationships. To address these issues, companies need to invest in the right tools and strategies, such as regular video meetings, instant messaging platforms, and clear communication guidelines.
Work-Life Balance Struggles
While remote work can improve work-life balance, it can also blur the lines between work and personal life. Without the physical separation of an office, it can be challenging for employees to “switch off” from work. This can lead to longer working hours and, eventually, burnout. To prevent this, employees need to set clear boundaries and establish routines that help them maintain a healthy balance.
Security Concerns
Another significant challenge of remote work is ensuring data security. Remote work environments can be more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, especially if employees are using personal devices or unsecured networks. Companies must implement strict security protocols, such as VPNs, multi-factor authentication, and regular security training, to protect sensitive information.
Conclusion
Remote work is no longer just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach work. While it offers numerous benefits, including increased productivity, cost savings, and access to a global talent pool, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed. As we move forward, it’s clear that remote work will continue to play a significant role in the future of work. However, its long-term success will depend on how well companies and employees can adapt to the evolving workplace dynamics.
FAQs
Is remote work more productive than office work?
Yes, many studies have shown that remote workers are often more productive than their office-based counterparts due to fewer distractions and a more flexible work environment.
What are the biggest challenges of remote work?
The biggest challenges include communication and collaboration issues, maintaining work-life balance, and ensuring data security.
How can companies ensure data security with remote work?
Companies can ensure data security by implementing strict security protocols, such as VPNs, multi-factor authentication, and regular security training for employees.
Will remote work continue after the pandemic?
Yes, remote work is expected to continue after the pandemic, with many companies adopting hybrid models or fully remote work policies.
What industries benefit the most from remote work?
Industries that benefit the most include technology, finance, consulting, and creative services, where work can be done effectively without a physical presence.





